Otoplasty: Ear Surgery
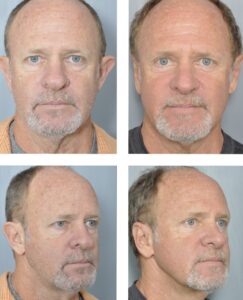
Otoplasty, commonly known as ear surgery, is a cosmetic procedure aimed at altering the appearance of the external ears. This surgery can involve various techniques such as ear pinning (bringing the ears closer to the head), reducing the size of large ears, or reshaping the cartilage to create more desirable contours.
The Procedure
Ear surgery typically takes about two to three hours and begins with an incision behind the ear, in the natural fold where the ear joins the head. The surgeon then removes the necessary amounts of cartilage and skin to achieve the desired effect. In some cases, the cartilage is trimmed and shaped, then secured with permanent absorbable tacks. In other instances, no cartilage is removed; instead, stitches are used to hold the cartilage in place. Absorbable tacks are applied to anchor the ear until healing occurs, ensuring it remains in the desired position.
Post-Surgery Considerations
After otoplasty, patients may experience a few minor complications. A small percentage might develop a blood clot on the ear, which can either dissolve naturally or be removed with a needle. There is also a risk of infection in the cartilage, which can lead to scar tissue formation. These infections are typically treated with antibiotics, but in rare cases, surgery may be necessary to drain the infected area.
The risks associated with otoplasty are minimal. Post-surgery, a thin white scar may form behind the ear, but it is usually inconspicuous due to its location in a natural crease.
Recovery
Recovery times for otoplasty are relatively short. Most adults can return to work about five days after surgery, while children can typically go back to school after about seven days. Otoplasty offers a safe and effective way to improve the appearance of the ears, with minimal risks and a quick recovery period.